
- Address : P.O. Box 11, Gannoruwa rd, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
- E- Mail : director.hordi@doa.gov.lk
- Telephone :(+94) 081-2388011-12-13
- Fax :(+94) 081-2388234

Cucumber
Cucumis sativus
Cucumber is a popular vegetable as a cooking type or salad type
Released Varieties
Climatic requirements/ Areas suitable for cultivation
Suitable to cultivate in wet zone in year round and dry zone in Maha season. Can be cultivated up to above 1000 m sea level. Optimum temperature is 30 O C.
Soil
Can be cultivated I with different soil types having better drainage and organic matter. Suitable pH is 5.5-7.5.
Seed requirement
1 kg/ha
Nursery Management
No nursery needed direct planting is practiced
Land preparation
After cleaning to remove weeds, hills can be prepared as 30m x30m x 30m in size.
Planting
Direct seeding
Spacing
1m x 1m as a spacing for mono culture. Sometime this crop can be cultivated as mix crop.
Fertilizer
| Time of application |
Urea kg/ha |
TSP kg/ha |
MOP kg/ha |
| Basal |
75 |
200 |
60 |
| After 4 weeks |
75 |
– |
60 |
| After 5 weeks |
75 |
– |
60 |
Water supply
Apply sufficient amount of water, without lodging
Weed Control
Need to remove weeds at initial stage, better to use mulch to control weeds.
Harvesting
Yield
15-20 t/ha OP varieties
25-30 t/ha Hybrid varieties
Pest Management
This description will be available soon…
Till then, please access the Sinhala language page on insect control through below link.
Disease Management
- Fungal diseases
- First appears as pale yellow spots on older leaves
- These spots enlarge as the white, fluffy mycelium grows over leaves surfaces
- Severely attacked leaves become brown and shrivelled and defoliation may occur
 |
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
- Distraction of infected plant debris after harvest
Causal organism: Pseudoperonospora cubensis
Symptoms:
- Angular yellow spots that are limited by the leaf veins on the upper surface of the leaves.
- Leaves become chlorotic and finally necrotic and host plant cells die
Management:
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
- Distraction of infected plant debris after harvest
Causal organisms: Sclerotium spp., Fusarium spp.
Symptoms:
- Initially the plants show temporary wilting symptoms
- The leaves yellowing, loose turgidity and show drooping
- Eventually, the plant dies.
- Vascular bundles in the collar region become yellow or brown.
Management:
- Destroy infected plants with soil
- Improved drainage
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
Causal organisms: Didymella bryoniae
Symptoms:
- Lesions on leaves and fruit usually begin as spreading water-soaked areas
- The former these may have a chlorotic halo, become light brown and irregular in outline
- Dark cracked sunken lesions on fruit
- Plant collapse where sunken, girdling cankers
- Spots on stems often elongate into streaks and gummy exudates may occur from cracks
- Dark brown to black fruiting bodies (pycnidia) can be seen on fruit, stem, or leaf
Management:
- Crop debris should be ploughed deeply immediately after harvest to reduce fungus survival
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
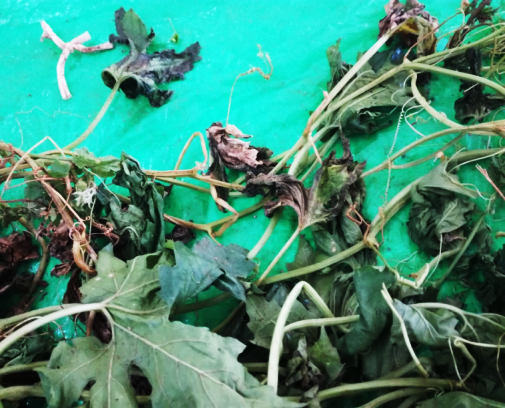
- Bacterial diseases
- Sudden drooping of leaves
- Whole plant finally wilts
- Leaves become brown, dry
- Vascular discoloration (Brown)
- Permanent wilting
- Infected soil, water, plant debris, Nematodes and insects ,pruning, Weeds as host plants
 |
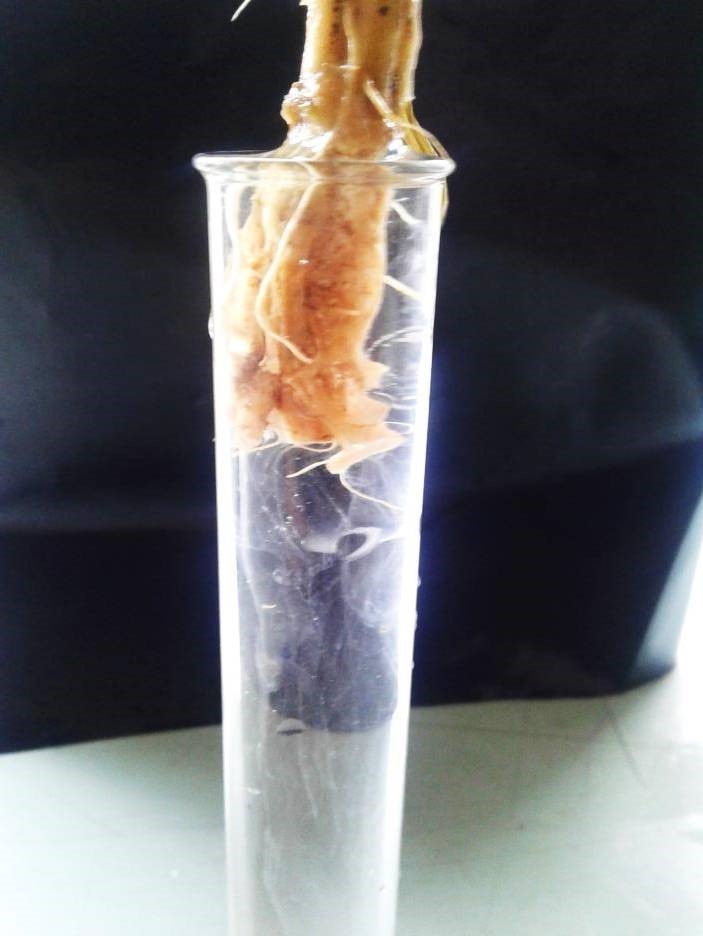 |
- Destroy infected plants with soil
- Crop rotation with non- susceptible crops (okra , maize)
- Mixed cropping with cruciferae crops
- Avoid movement of equipment from infected fields to non- infected fields
- Viral diseases
- upward curling, shortening, and distortion of leaves
- Plant stunted and fruits deformed.
 |
- Mosaic and mottling of leaves
- leaf distortion
- Malformation of fruits and reduction in fruit size
- In severe infections, oily patches on the fruit surface
 |
Transmission: Seed borne, through sap
Symptoms:
- Green mottle, leaf deformation
- Green spot on fruits, turn bright yellow and decaying fruit
- fruit malformation.
Symptoms:
- Stunting, yellowing, necrosis (occasionally), mosaic, leaf deformations (blisters, shoe stringing)
- Fruit discolorations and deformations
- Pytoplasma Disease
- Smaller, thickened and yellowish green leaves
- Shortened internodes and stunting of plants
- Witch’s broom symptom
- Greening of flowers
- Through leaf hoppers
- Through infected seeds
- Remove infected plants
- Control vectors (leaf hoppers) using a recommended insecticide
 |
 |
