
- Address : P.O. Box 11, Gannoruwa rd, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
- E- Mail : director.hordi@doa.gov.lk
- Telephone :(+94) 081-2388011-12-13
- Fax :(+94) 081-2388234

Snake Gourd
Trichosanthes cucumerina L
Originated in tropical Asian countries . Found in South and Southeast Asia, including India , Bangladesh , Nepal , Pakistan , Sri Lanka , Indonesia , Malaysia , Burma and southern china.
In dry zone crop is cultivated in yala season. In wet zone crop is cultivated throughout the year. This crop has some medicinal values especially in ayurwedic medicine.
Released Varieties
Climatic requirements/ Areas suitable for cultivation
High temperature is preferred. cultivated up to 500m elevation . successfully cultivated in Mathale, kandy, Hambanthota, Kurunegala, Rathnapura
Soil
Soil with high organic matters and good drainage is need. pH should be 5.5 -7.5
Seed requirement
4kg/ha
Nursery Management
Direct planting of seeds in the field
Land preparation
Plough the land 20-30 cm depth. 30 x 30 x 30 cm holes are prepared with recommended spacing
Planting
Add organic matters and fill the holes. Plant 2 seeds in one hole, with 2-3 cm depth seed germinate starts within 5 – 8 days
Spacing
1.5 m x 1.5 m
Fertilizer
Add 10 t/ha of organic matters. Add basal , 2-3 days before planting and add top dressing 4 and 8 weeks after emergence of seedlings
Fertilizer recommendation for 1ha
Time of Application | Urea kg/ha | TSP kg/ha | MOP kg/ha |
Basal | 75 | 200 | 60 |
Top Dressing One (4weeks after planting) | 75 | – | 60 |
Top Dressing Two (8 weeks after planting) | 75 | – | 60 |
Water supply
Daily irrigate the crop until seed germinate
Weed Control
Control weeds at the early stages of the crop
Harvesting
Harvest the crop 60-75 days after planting with 4 days interval
Yield
20,000 kg/ha
Training
Train the vine 2m heights trellis. Remove side branches.
Pest Management
Disease Management
- Fungal diseases
- First appears as pale yellow spots on older leaves
- These spots enlarge as the white, fluffy mycelium grows over leaves surfaces
- Severely attacked leaves become brown and shrivelled and defoliation may occur
 |
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
- Distraction of infected plant debris after harvest
Causal organism: Pseudoperonospora cubensis
Symptoms:
- Angular yellow spots that are limited by the leaf veins on the upper surface of the leaves.
- Leaves become chlorotic and finally necrotic and host plant cells die
Management:
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
- Distraction of infected plant debris after harvest
Causal organisms: Sclerotium spp., Fusarium spp.
Symptoms:
- Initially the plants show temporary wilting symptoms
- The leaves yellowing, loose turgidity and show drooping
- Eventually, the plant dies.
- Vascular bundles in the collar region become yellow or brown.
Management:
- Destroy infected plants with soil
- Improved drainage
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
Causal organisms: Didymella bryoniae
Symptoms:
- Lesions on leaves and fruit usually begin as spreading water-soaked areas
- The former these may have a chlorotic halo, become light brown and irregular in outline
- Dark cracked sunken lesions on fruit
- Plant collapse where sunken, girdling cankers
- Spots on stems often elongate into streaks and gummy exudates may occur from cracks
- Dark brown to black fruiting bodies (pycnidia) can be seen on fruit, stem, or leaf
Management:
- Crop debris should be ploughed deeply immediately after harvest to reduce fungus survival
- Use recommended fungicides at initial stage of disease development (Refer: Pesticide recommendation DOA, 2019)
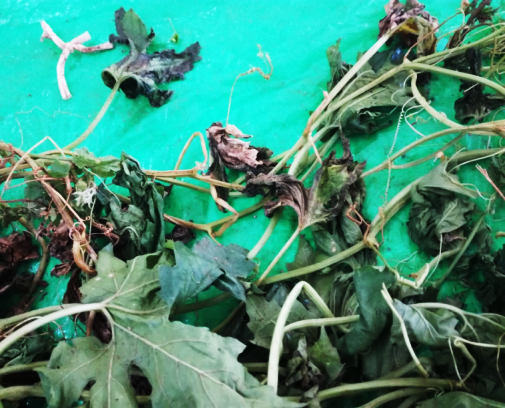
- Bacterial diseases
- Sudden drooping of leaves
- Whole plant finally wilts
- Leaves become brown, dry
- Vascular discoloration (Brown)
- Permanent wilting
- Infected soil, water, plant debris, Nematodes and insects ,pruning, Weeds as host plants
 |
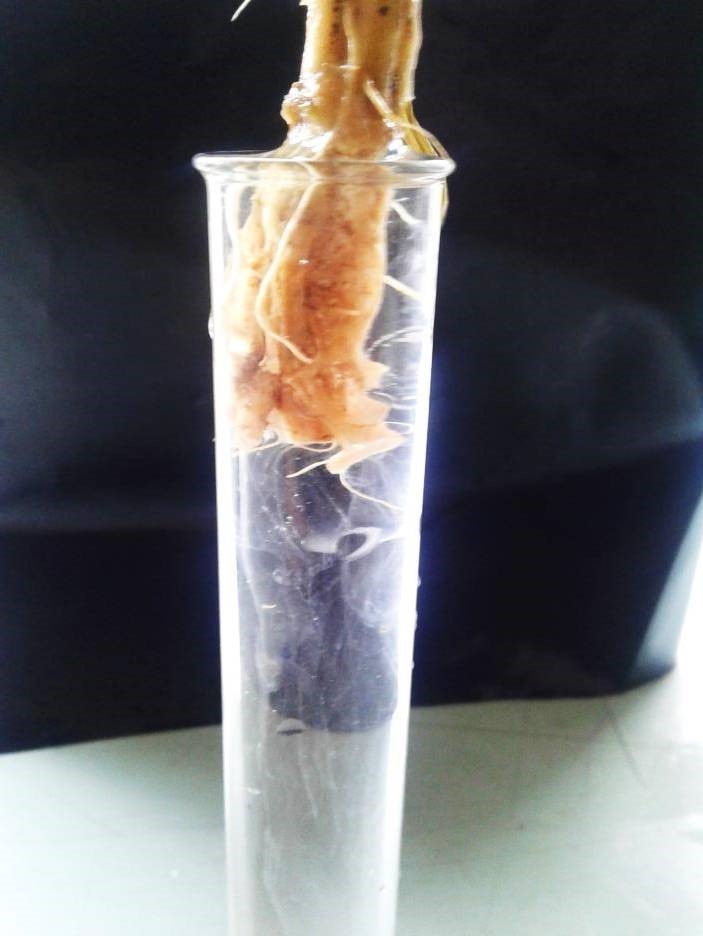 |
- Destroy infected plants with soil
- Crop rotation with non- susceptible crops (okra , maize)
- Mixed cropping with cruciferae crops
- Avoid movement of equipment from infected fields to non- infected fields
- Viral diseases
- upward curling, shortening, and distortion of leaves
- Plant stunted and fruits deformed.
 |
- Mosaic and mottling of leaves
- leaf distortion
- Malformation of fruits and reduction in fruit size
- In severe infections, oily patches on the fruit surface
 |
Transmission: Seed borne, through sap
Symptoms:
- Green mottle, leaf deformation
- Green spot on fruits, turn bright yellow and decaying fruit
- fruit malformation.
Symptoms:
- Stunting, yellowing, necrosis (occasionally), mosaic, leaf deformations (blisters, shoe stringing)
- Fruit discolorations and deformations
- Pytoplasma Disease
 |
 |
