
- Address : P.O. Box 11, Gannoruwa rd, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
- E- Mail : director.hordi@doa.gov.lk
- Telephone :(+94) 081-2388011-12-13
- Fax :(+94) 081-2388234

Potato
Solanum tuberosum
Potato is belong to solanacea family. It was introduced to Sri Lanka by Samuel Baker in 1850. Large Scale cultivation of potato was started by Department of Agriculture in Rahangala farm but it was failed due to bacterial wilt. Farmers multiply potato seeds on land in higher elevation for producing seeds for the major cultivation season (Yala season).
Released Varieties
Climatic requirements/ Areas suitable for cultivation
Tuber initiation of potato requires low soil temperature less than 24 oC. Day and night temperature difference should have more than 10 oC for successful crop. Potato grows well in up country area whereas heat tolerance varieties can be grown in dry areas such as Jaffna and Kalpitiya.
Soil
Well drain soil with more organic matter is required. Suitable pH range is 5.5-6.6.
Seed requirement
2000 kg tubers /ha
Nursery Management
N/A
Land preparation
Plough soil to the depth of 30 cm and add lime if pH is low.
Planting
Potato tubers can be planted in ridges or raised beds. Soil earthing up is carried out 30 days after planting
Spacing
60 x 25 cm
Fertilizer
For up lands of Nuwara Eliya and Badulla districts and calcic red latosols soil of Jaffna district;
| Times for apply | Urea kg/ha | TSP kg/ha | MOP kg/ha |
| Basal fertilizer | 55 | 270 | 125 |
| Top dressing (2 weeks after planting) | 110 | – | – |
| Top dressing (3-4 weeks after planting) | 165 | – | 125 |
For rice based cropping system of Nuwara Eliya and Badulla districts;
| Times for apply | Urea kg/ha | TSP kg/ha | MOP kg/ha |
| Basal fertilizer | 55 | 270 | 85 |
| Top dressing (2 weeks after planting) | 110 | – | – |
| Top dressing (3-4 weeks after planting) | 165 | – | 85 |
For regosols of Kalpitiya;
| Times for apply | Urea kg/ha | TSP kg/ha | MOP kg/ha |
| Basal fertilizer | – | 270 | – |
| Top dressing (2 weeks after planting) | 65 | – | 50 |
| Top dressing (4, 6 & 8 weeks after planting) | 90 | – | 70 |
Water supply
Tuberization and tuber bulking stages are critical for water supply. High yielding crop required about 70 % available water. Sprinkler or drip irrigation methods are more suitable than the furrow irrigation.
Weed Control
Pre-emergent herbicide: metribuzine can be spray to control weeds. Weeds also control by intercultural operations at 2 and 4 weeks after planting.
Pest Management
 |
 |
 |
- Regular field inspection
- Yellow colour sticky trap
- Covering crops with suitable material prevent mitigating flies
- Removal of other host plants surrounds the crop field
- Removal and distraction of infected plant material
- Augment ecto-parasitoid Diglyphus isaea
- Encourage naturally found parasitoids Hemiptarsenus semibiclavas and Opius spp
- Azadiractin 1% EC at the rate of 16ml/16 l of water
- Abamectin 18g/l EC at the rate of 9.6 ml/16 l of water
- Neem seed water extract at the rate of 640g/16 l of water
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Regular monitoring
- Healthy seed tubers to be planted slightly deeper
- Proper earthing up to avoid exposing tubers
- Crop rotation
- Discourage growing of alternate host plants
- Proper irrigation to prevent soil cracks and soil spaces are
- Removing all tubers from fields at harvesting
- Destruction of residues and maintain proper field sanitation
- Chlorantraniliprole20%+Thiamethoxam 20%WG at the rate of 5g per 16l of water
- Reject seed lots from fields or storage that had been infested with PTM
- Maintain proper Storage sanitation
- Tubers must be undamaged and free from soil or other residues
- Tubers should be kept at cold store
- Application of seed treatments- Thiocyclam (Hydrogen Oxalate) 50% SP-40g/100Kg of seeds
- Pirimiphose methyl 500g/l EC at the rate of 64 ml per 16 l of water
- Acetamiprid 200g/l SP at the rate of 16 ml per 16 l of water
- Novaluron 100g/l EC at the rate of 16 ml per 16 l of water
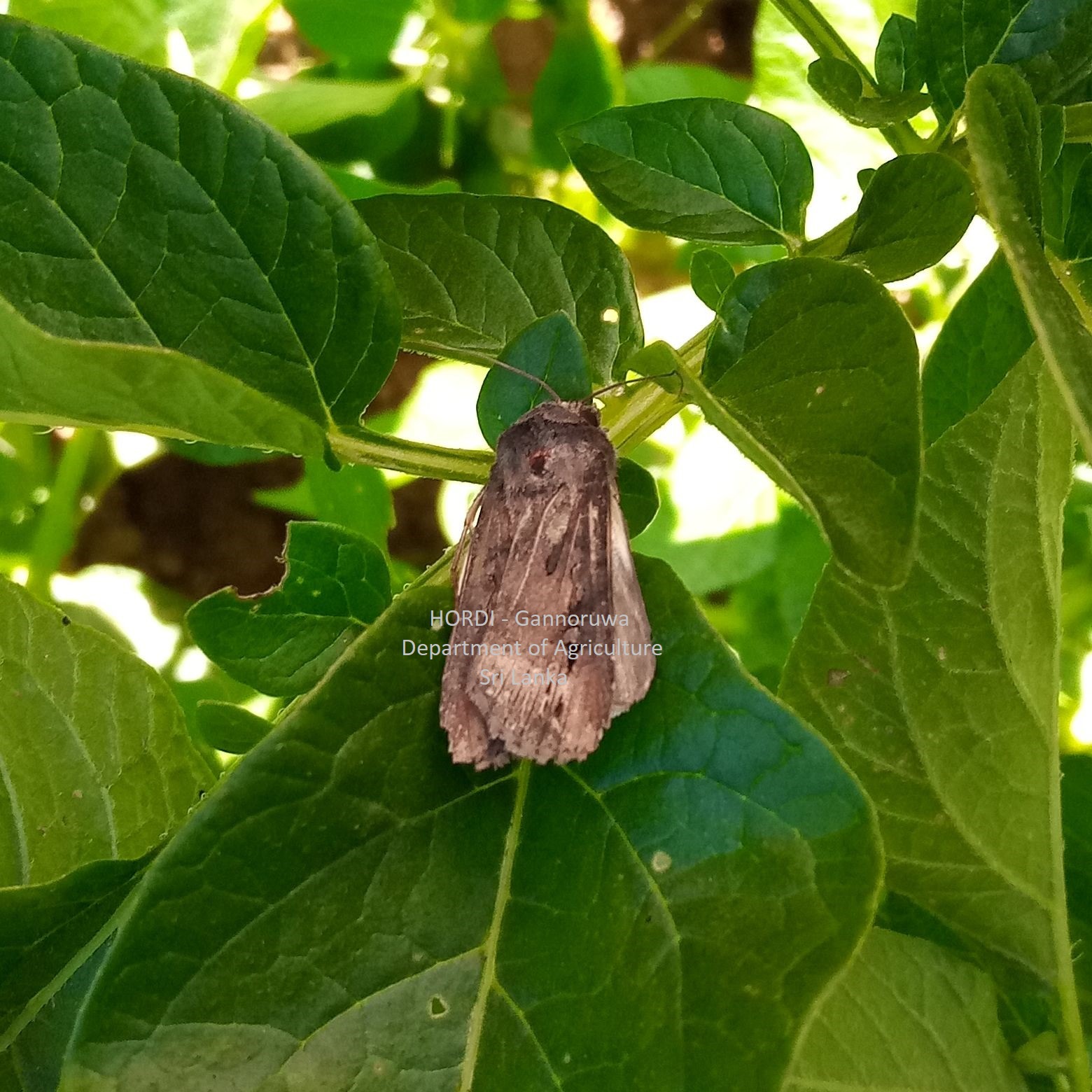 |
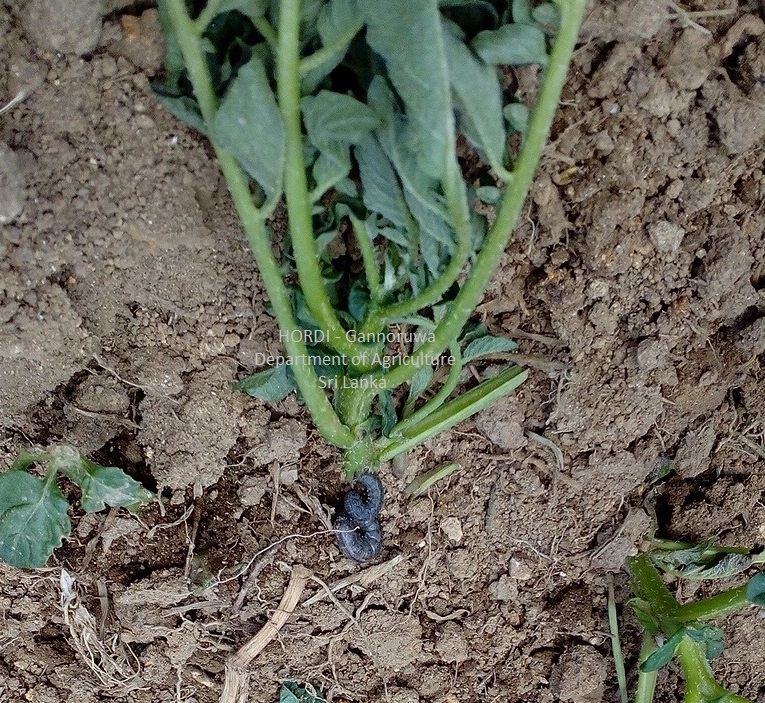 |
 |
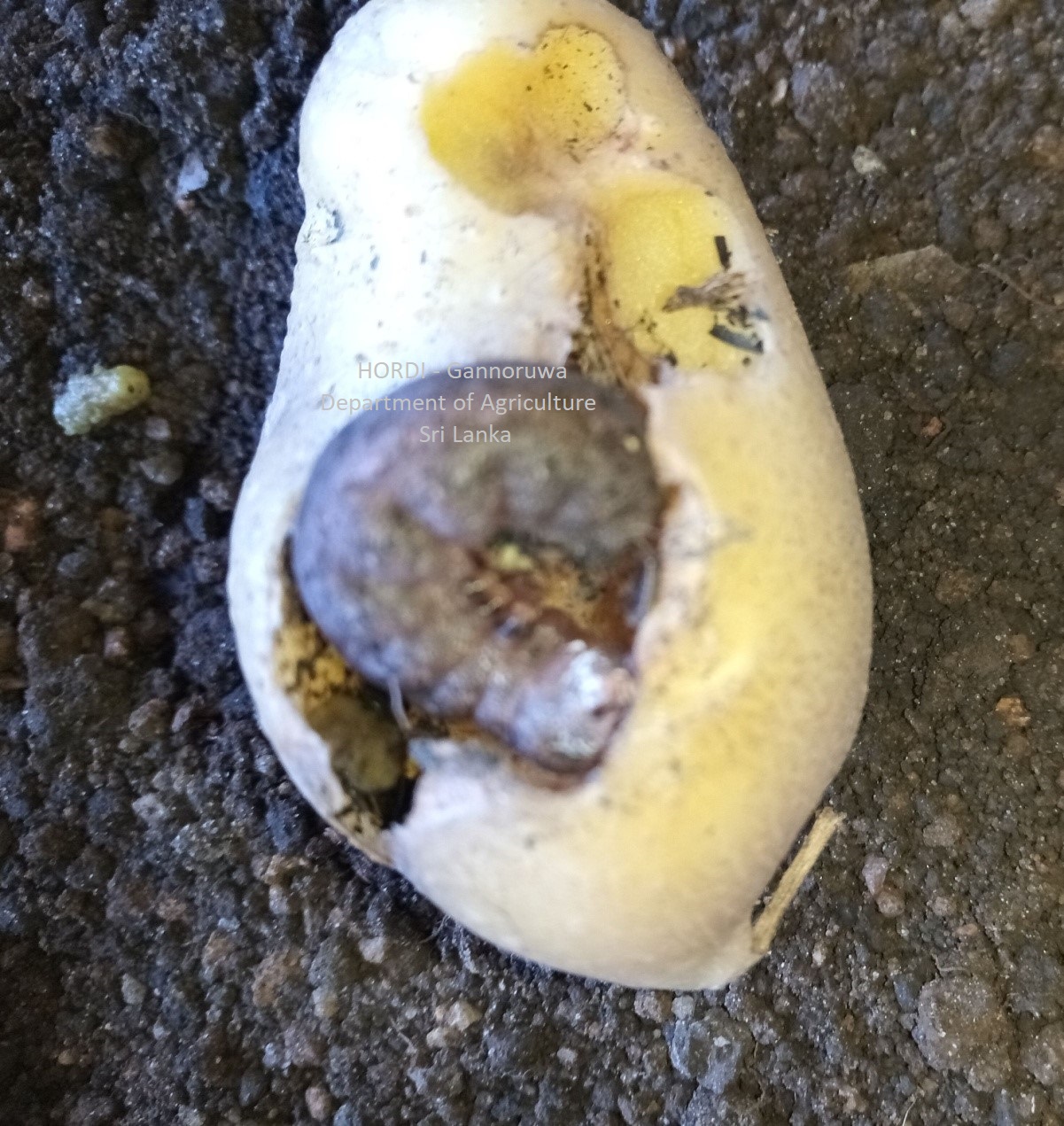 |
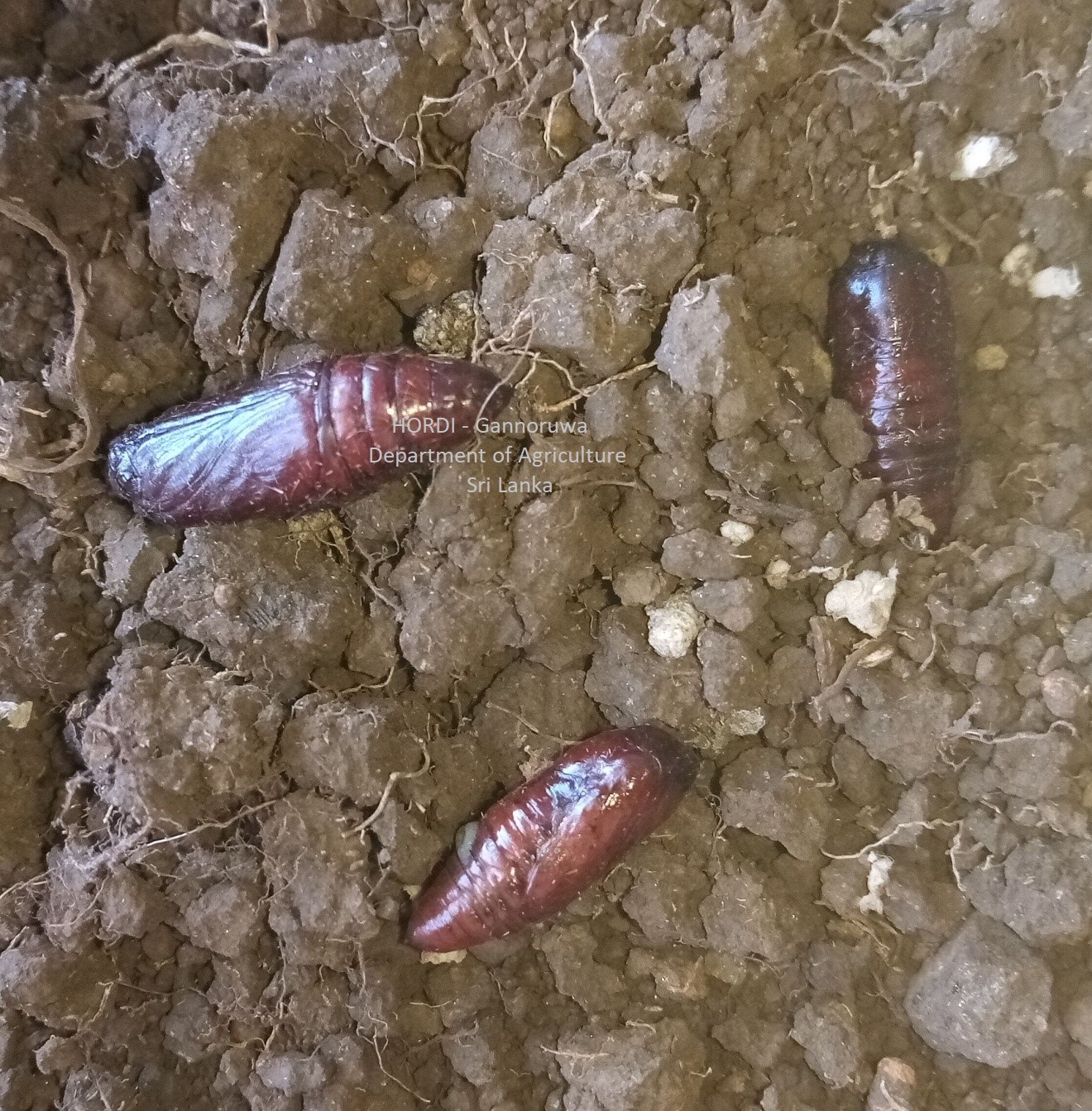 |
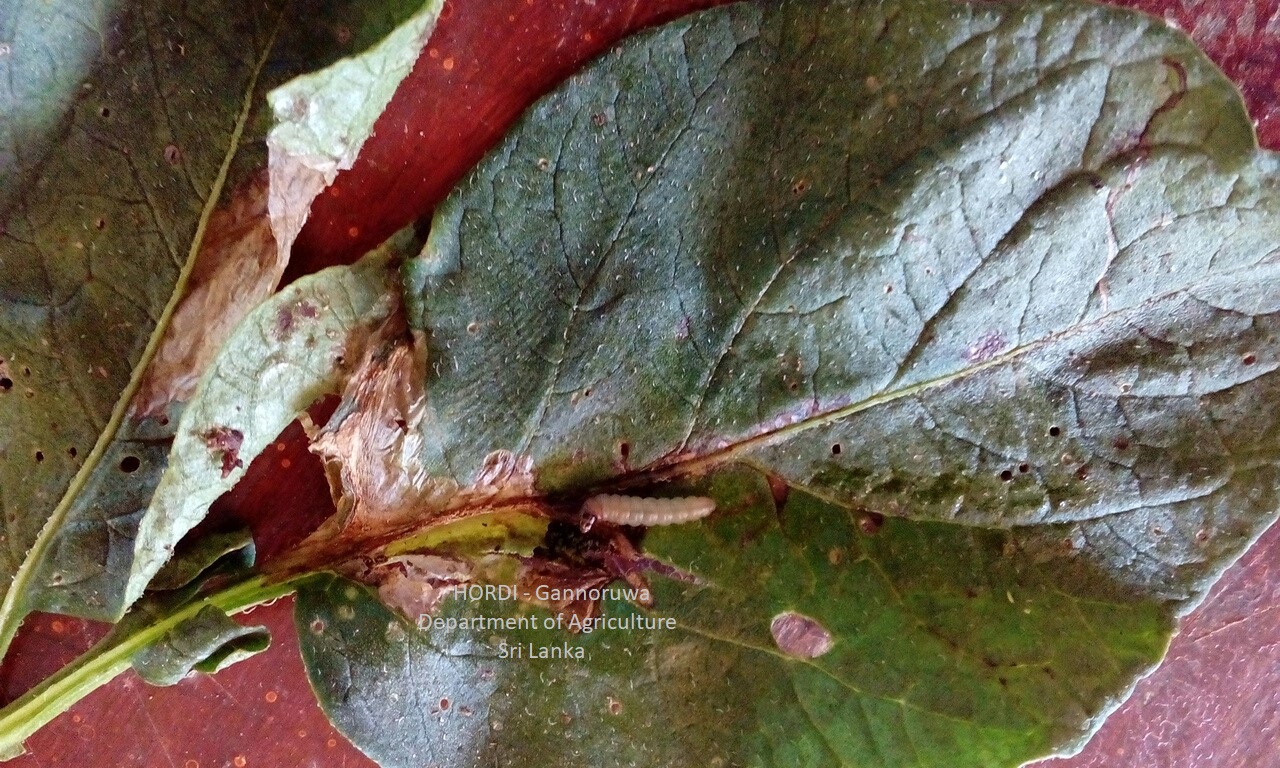
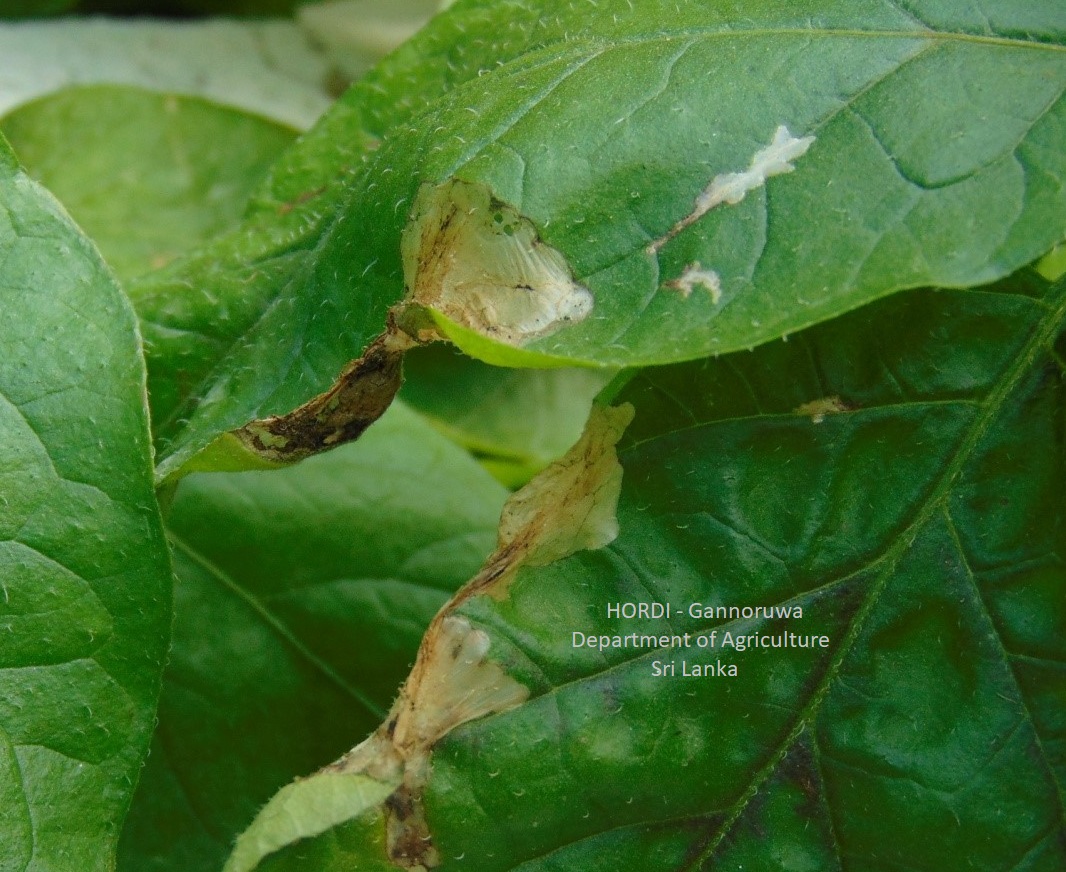
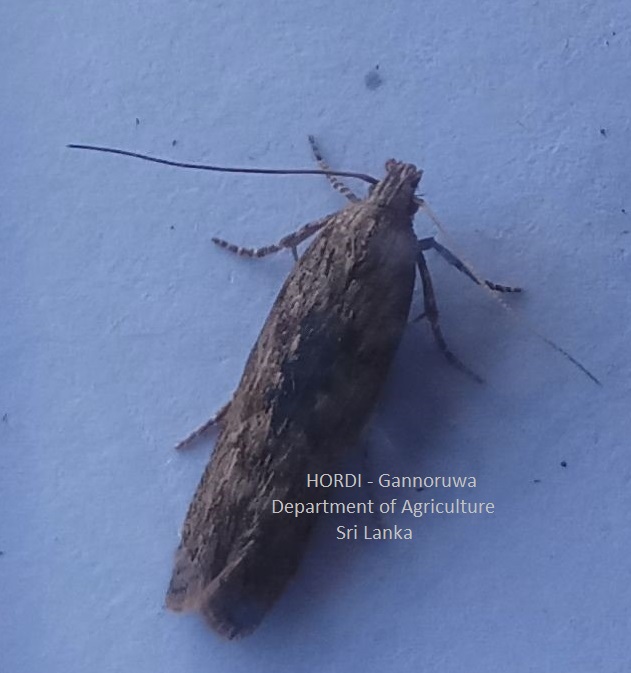
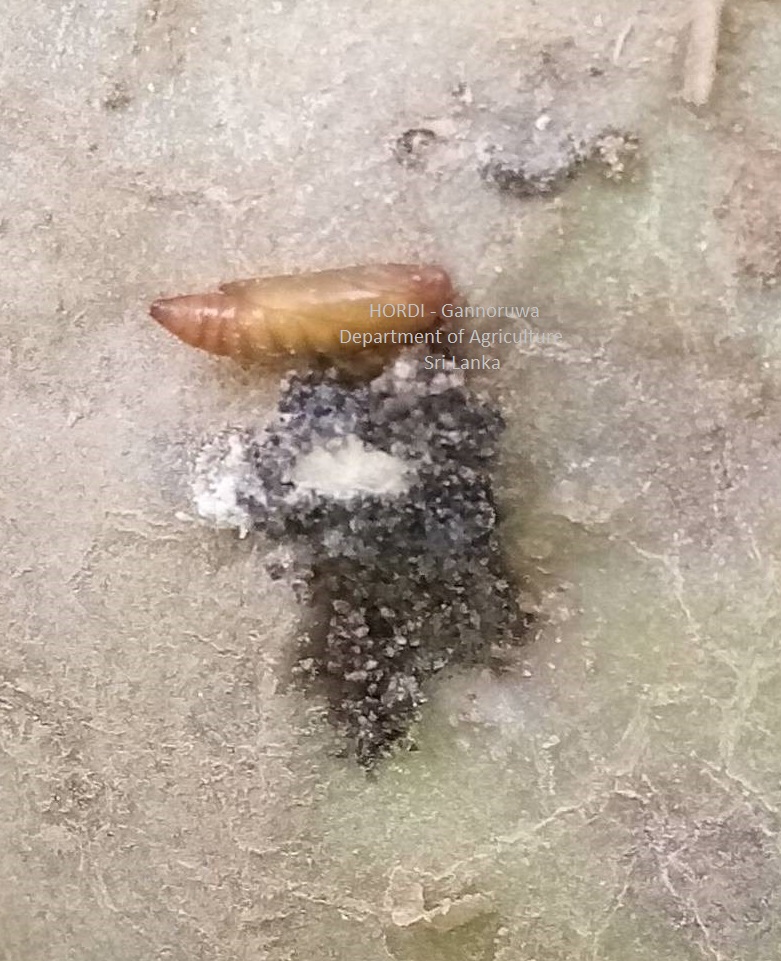
- Regular monitoring
- Hand collecting and destroying
- Weed management
- Proper field sanitation
- Plough the soil deeply to bring the larvae and pupa to the surface of the soil
- Encourage predatory birds to preying the worms during tillage operation
- Profenophos 500 g/l EC at the rate of 32 ml per 16 l of water
- Etofenprox 100g/l EC at the rate of 24 ml per 16 l of water
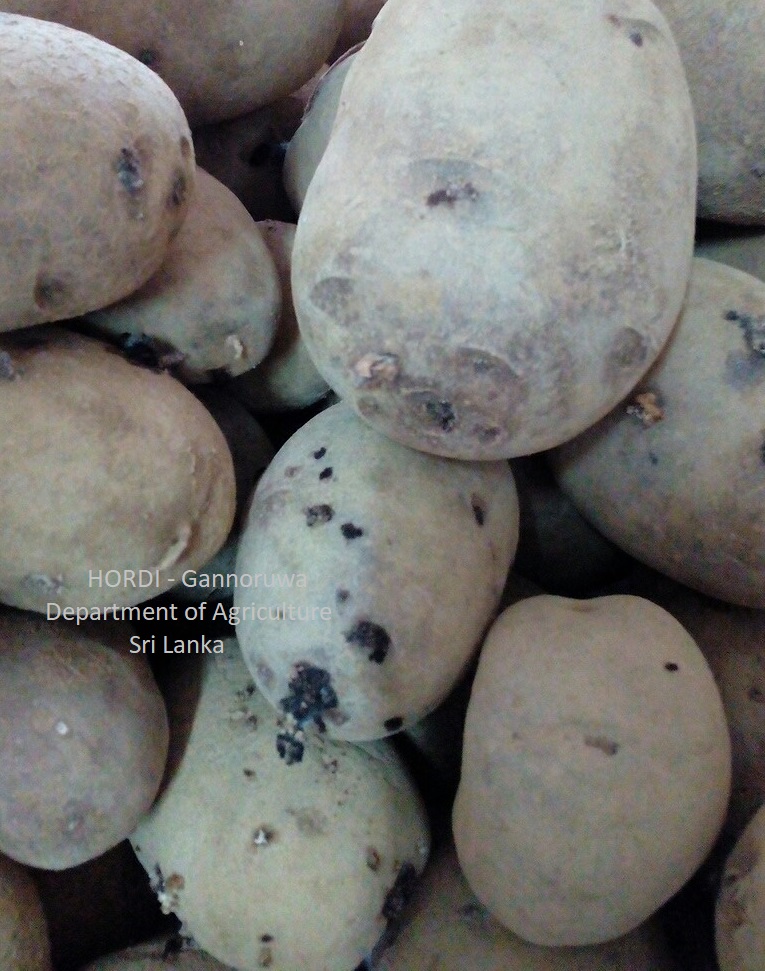
Damage Symptoms
Nematode remove nutrient from the roots and diminish supply of nutrient and water to the stems and leaves by injuring the roots and stunning their growth. Moderately infested plants normally have reduced tuber size. Heavily infested plants develop poorly and show yellowing of plants. Temperature become wormer, wilting of plants occurs.
Management
There are three basic challenges in managing PCN.
- Keeping potato land free of PCN
- Preventing lightly infested land from becoming heavily infested
- Bring high populations back to manageable levels
Follow the instruction below if the land is not infested
- Use certified seeds from DOA
- Avoid use of seed potatoes, soil and agriculture implements from infested land
- Treat the seed with 1% Sodium Hypochlorite solution for 25-30 minutes before planting
- Soil testing before planting
- Use interval between potato crops
- Preventing lightly infested land from becoming heavily infested
- Crop rotation
- Fallowing
- Avoid cultivation potato or solanaceous crops two or three seasons
- Use of resistant varieties
- Repeated sampling and determine the whether management is working
- Bring high populations back to manageable levels
- Apply Calcium hypochlorite at the rate of 70Kg/ha
Other than that educated farmers on the followings are more important
- Importance of PCN as a potato pest
- Easy method to detect PCN
- Control methods
- Prevent spread of PCN to new land
 |
 |
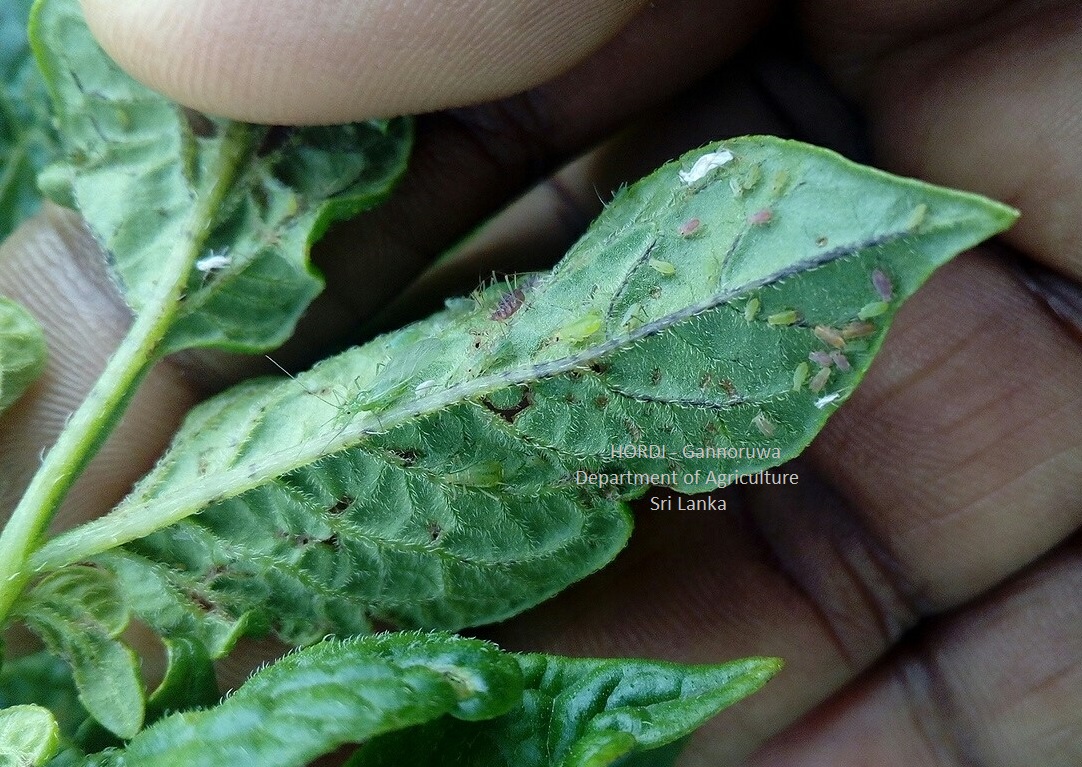
- Monitoring aphids’ population visually or placing yellow colour water trap.
- Weed control in crop fields to reduce the availability of alternate host plants
- Protect the predators and parasitoids by avoiding the use of broad-spectrum pesticides unnecessarily
- Thiamethoxam 25% WG at the rate of 5g per 16 l of water
- Imidacloprid 70%WG at the rate of 2g per 16 l of water
- Thiocyclam (Hydrogen Oxalate) 50% SP at the rate of 40g per 16 l of water
- Chlorantraniliprole 20% + Thiamethoxam 20% WG at the rate of 5g per 16 l of water
- Buprofezin 25% SC at the rate of 45ml per 16 l of water
- Azadirachtine 5%EC at the rate of 16ml per 16 l of water
Damage symptoms
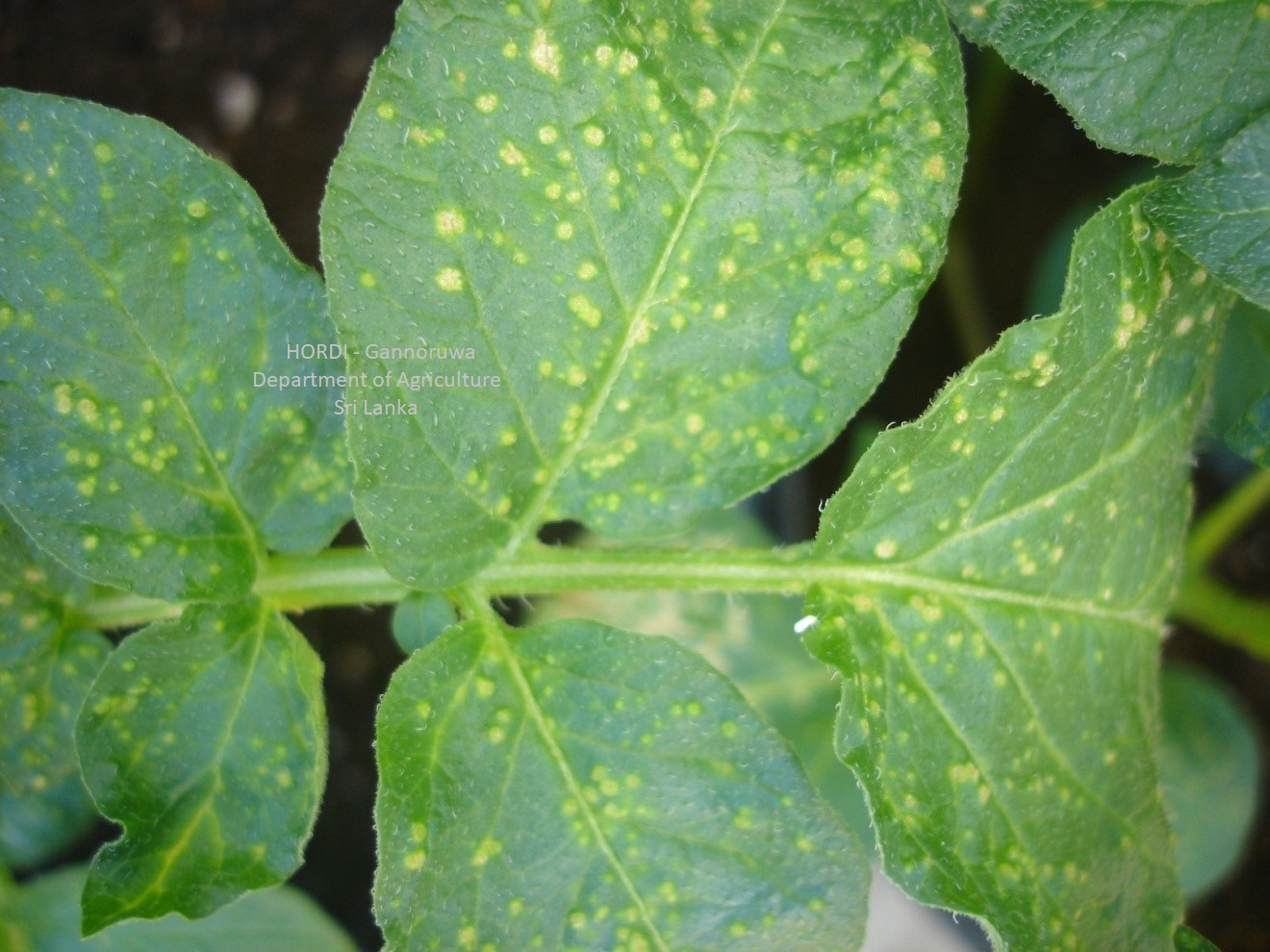
Thrips feed on potato leaves by rasping plant cells and sucking out its contents. Feeding on leaves caused deformities of the crop. Commonly found on the underside of leaves. Distinctive silvery or bronze scarring on the surfaces of the stems or leaves where the thrips feed
Management
- Weed control in crop fields to reduce the availability of alternate host plants
- Protect the predators and parasitoids by avoiding the use of broad-spectrum pesticides unnecessarily
- Planting at correct time
- Crop rotation
Chemical control
- Thiamethoxam 25% WG at the rate of 5g per 16 l of water
- Imidacloprid 70%WG at the rate of 2g per 16 l of water
- Thiocyclam (Hydrogen Oxalate) 50% SP at the rate of 40g per 16 l of water
- Chlorantraniliprole 20% + Thiamethoxam 20% WG at the rate of 5g per 16 l of water
- Buprofezin 25% SC at the rate of 45ml per 16 l of water
- Azadirachtine 5%EC at the rate of 16ml per 16 l of water
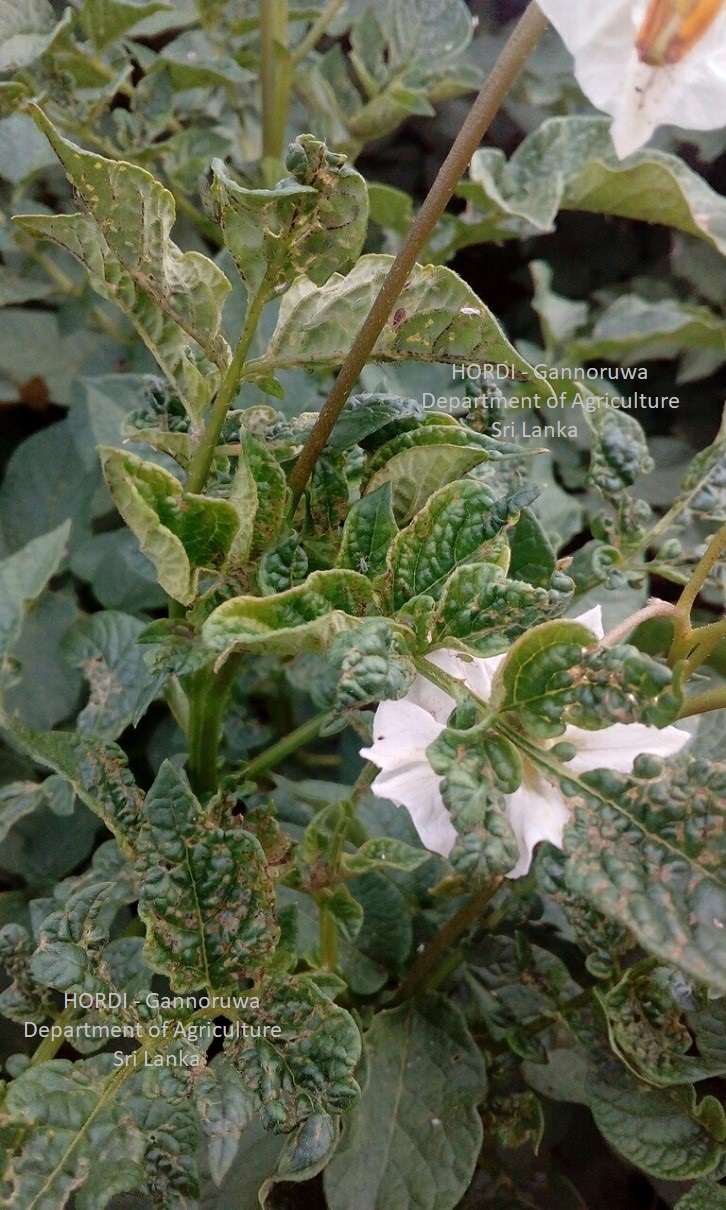
Damage symptoms
The adults and nymphs suck the plant sap and reduce the vigor of the plant. In severe infestations, the leaves turn yellow and drop off. When the populations are high they secrete large quantities of honeydew, which favors the growth of sooty mould on leaf surfaces and reduces the photosynthetic efficiency of the plants.
Management
- Maintain a high standard of weed control in crop fields to reduce the availability of alternate host plants
- Use yellow/blue sticky traps (Hang the traps slightly above or at the canopy level for better trapping)
- Spraying water – useful in dislodging adults
Chemical control
- Thiocyclam (Hydrogen Oxalate) 50% SP at the rate of 40g per 16 l of water
- Chlorantraniliprole 20% + Thiamethoxam 20% WG at the rate of 5g per 16 l of water
- Buprofezin 25% SC at the rate of 45ml per 16 l of water
- Azadirachtine 5%EC at the rate of 16ml per 16 l of water
These pests are recorded as occasional pest.
Damage symptoms
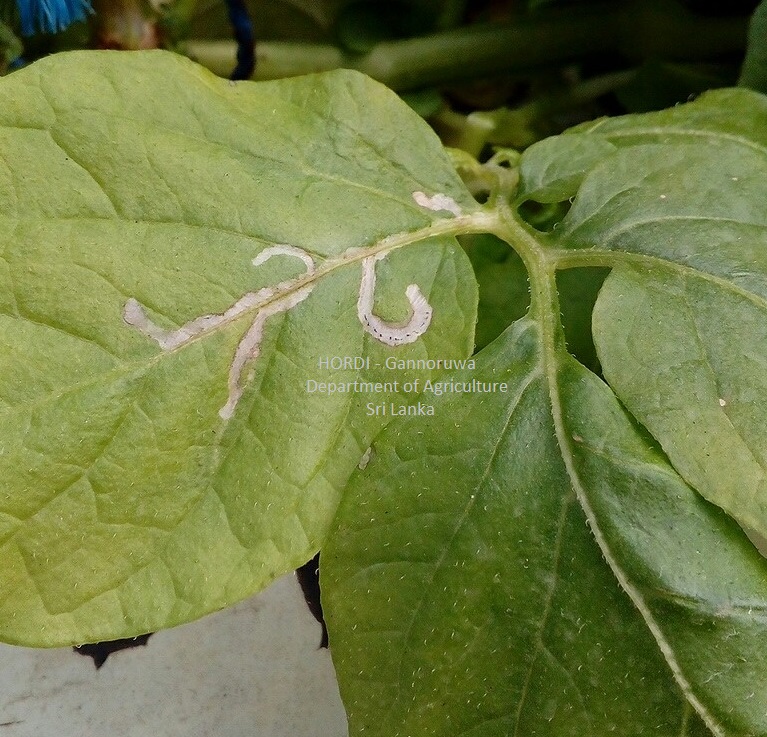
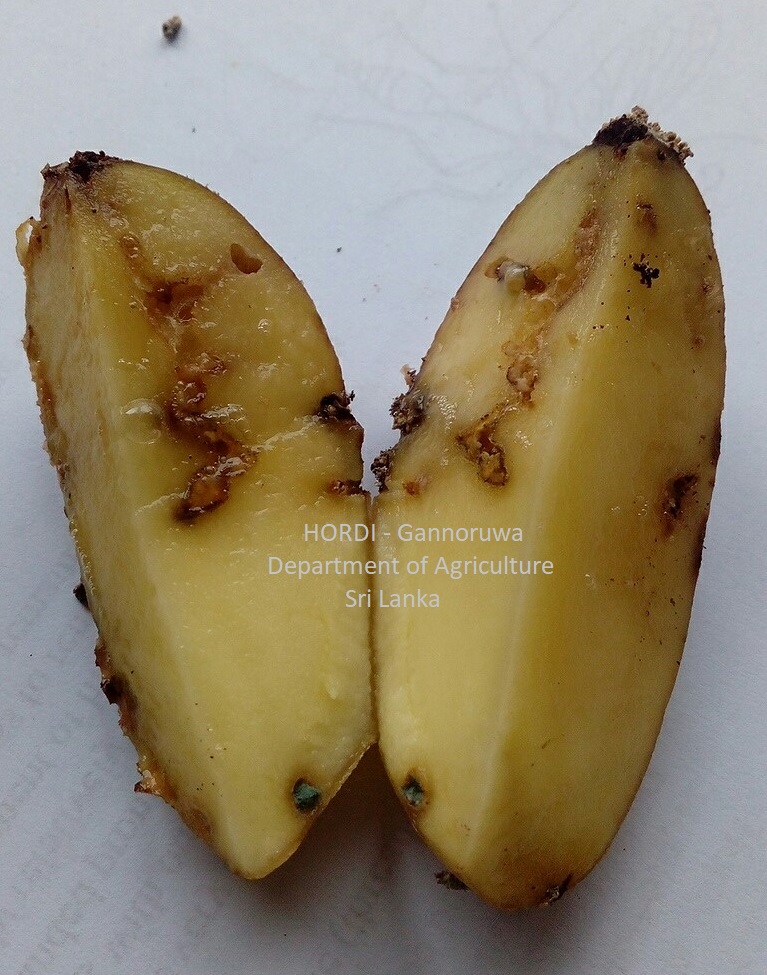
The larvae damage roots, stems and tubers and reduce the market quality of tubers.
Management
- Plough the soil deeply to bring grubs to the surface
- Encourage predatory birds to preying the worms during tillage operation
- Crop rotation
- Increase field sanitation
- Application of properly decomposed FYM(Farm Yard Manure) /compost at recommended dose
Damage symptoms
Create irregular holes with smooth edges on leaves and destroy tender leaves. Damage is common during rainy weather or an abundance of weed growth.
Management
- Eliminate place where can shelter during day time
- Regular practice of trapping and removing snails
- Removing debris and manage field sanitations
- Proper weed management
- Regular field infection and hand collection
- Encourage predatory birds by enhancing natural habitats
Chemical control
- Metaldehyde 5% GR at the rate of 10-40 Kg/ha
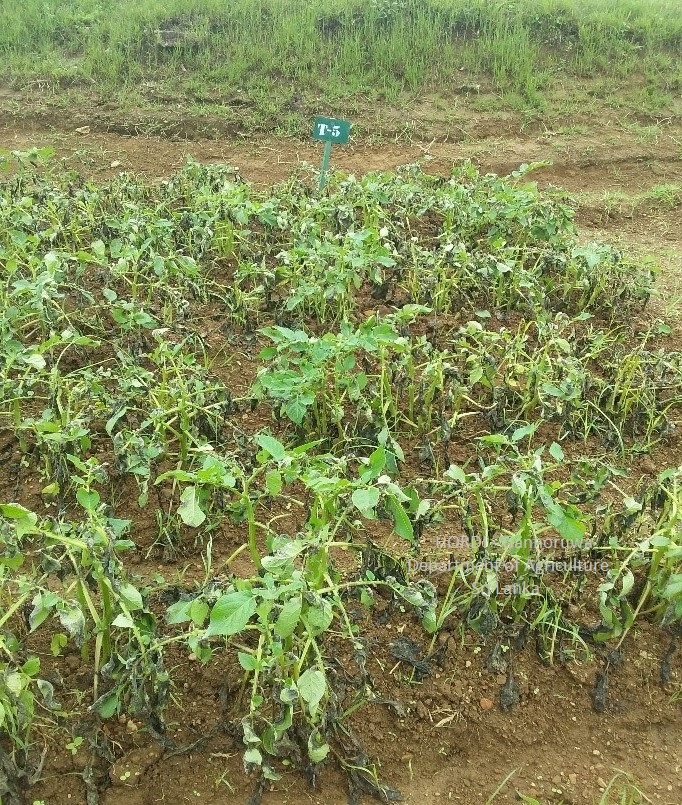
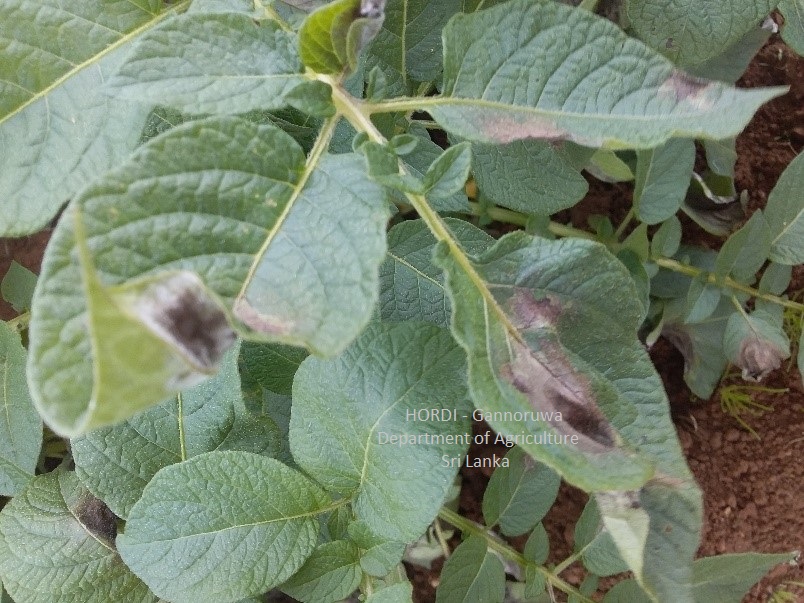
Disease Management
- Crop rotation/Fallowing
- Start cultivation at correct time
- Use resistant varieties – Carlous
- Use disease free tubers
- Application of Fungicides – Mancozeb, Maneb, Metalaxyl, Fluazinam
 |
 |
- Crop rotation
- Application of fungicides – Mancozeb, Maneb
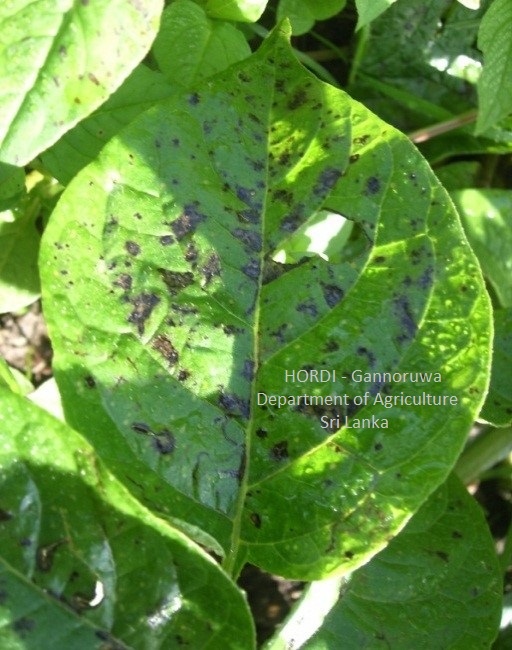 |
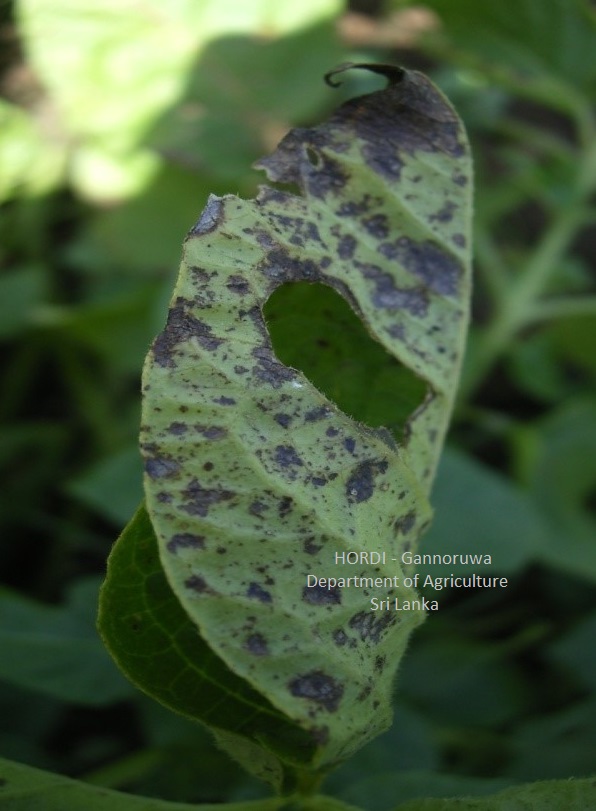 |
- Use disease free tubers
- Maintain soil pH 5.0- 5.2
- Maintain soil water level
- Crop rotation
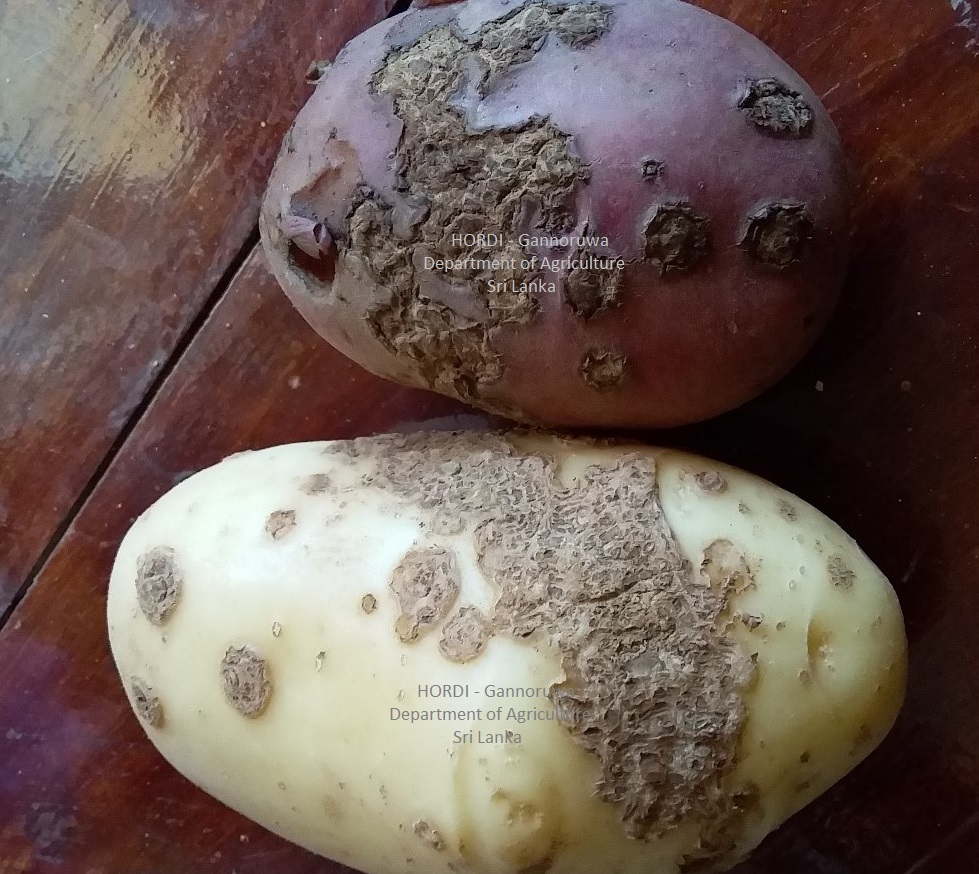 |
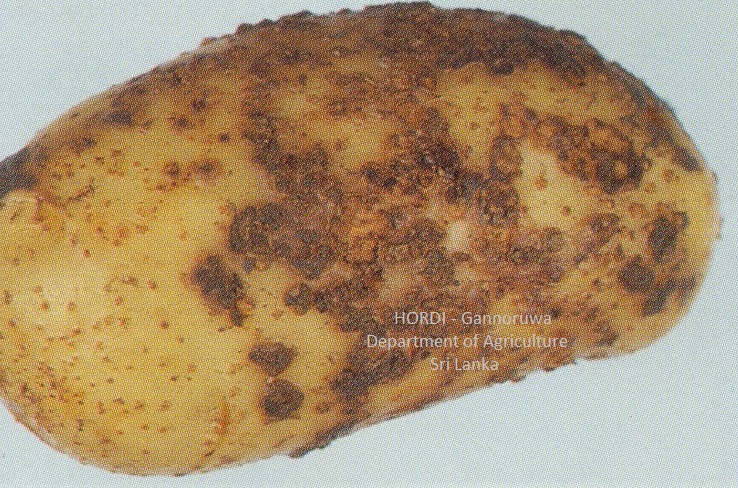 |
- Crop rotation
- Use disease free tubers
- Crop rotation/Fallowing
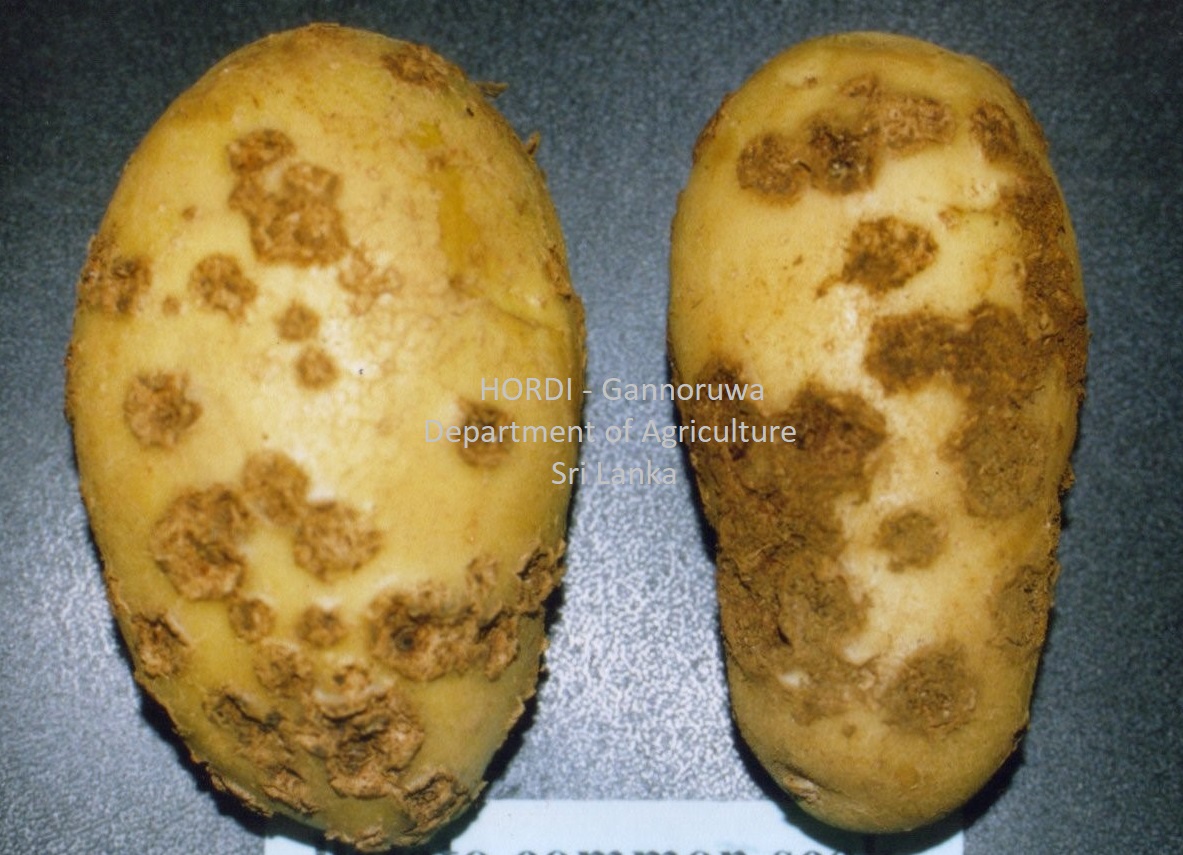 |
- Use disease free tubers
- Crop rotation/fallowing – at least three years
- Improve drainage in the fields
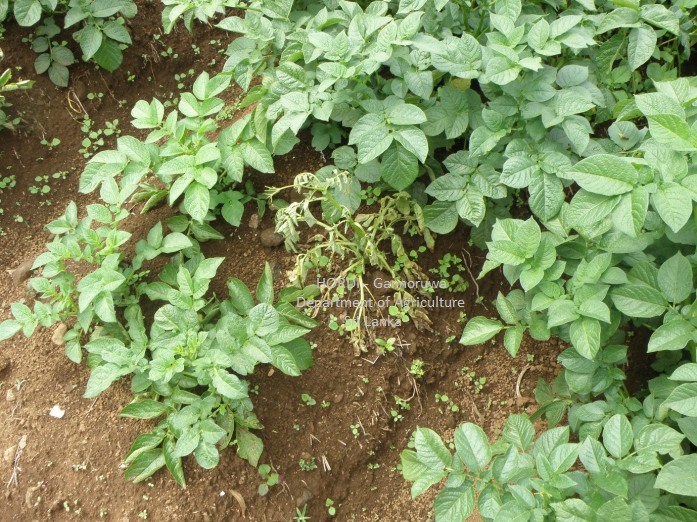 |
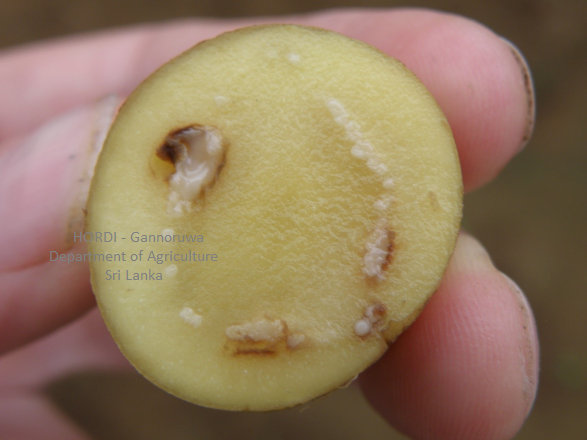 |
- Use disease free tubers
- Crop rotation
- Control vectors – aphids
- Regular monitoring the field
- Remove and destroy infected plants
Harvesting
Haulms should be removed 2 weeks before harvesting for maturing tubers
Yield
20-25 t/ha

