A phytosanitary certificate is a document which confirms the health status of a plant material (Plant or plant product) that are exported to a country. The certificate is issued by the NPPO of the country of export confirming required import conditions requested by the country of import.
- Register at National Plant Quarantine Service as an exporter. (after this all the registration consignments exported via seaport PQS prior to shipping date)
- Request made by exporter to obtain Phytosanitary certificate
Registration of request
- Investigating the request and inform the relevant officers (Entomology/Pathology/Treatment Technology/ Weed Science) for nursery or factory inspection.
- Coordinating the nursery/factory inspection & sampling considering the additional declarations and the date of dispatch of the consignment.
- Preparation of format for test report and distribute among the relevant laboratories.
- Collection of test report prior to date of export and inform contaminants of to the exporter.
- Preparation of final test report and send to exit point to issue phytosanitory certificate prior to date of dispatch.
- International agreement is that only authorized officers of the official plant protection service shall issue the phytosanitary certificate for all plant commodities exported.
- Phytosanitary certificates are prepared according to the model given by IPPC.
- A PSC is issued in three copies in English only. The original and a copy are kept in office and a copy is given to the applicant.
- Two different formats are available as Phytosanitary certificate and phytosanitary certificate for re export.
- Fulfill the import conditions commodities (Lab testing, visual inspection etc.)
- If you require special lab tests has to be done at central laboratories of NPQS (for this a separate request has to be made by the exporter)
- Lab test report is communicated to relevant entry port PQS by NPQS
- Bring entire consignment to Plant Quarantine station.
If Air Freight
- Compliance inspection test to inform the identify of consignment.
- All the boxes should be numbered; numbers are clearly mentioned in packing list.
If Sea Freight
- For a consignment prior registered with PQS at seaport.
- Either lab tests or not
- If Lab tested test report has to be received by the PQS, Seaport
- Consignment has to be transferred to port premises or shipping go down from factory.
- Request for Sample testing by PQS samples submission for testing (Only to understand the compliance of commodity with document evidence)
- Sample testing/inspection only if other requirements are fulfilled.
- Exporter will receive a notice/ approval to load the consignment to ship (prior approval)
- Exporter can submit consignment to vessel – obtain bill of lading.
- Submit bill of lading and application to obtain a PSC to PQS, seaport.
- PSC will be issued based on compliance inspection.
- Tea
- Rubber
- Spices
- Coir
- Vegetables
- Live plants etc:-
- Aquatic plants
- beetle leaves
- Cut foliage
- Coconut/Coconut products
- Cut flowers
- Live Plants
- Rooted cuttings
- Spices
- Tea, Tobacco
- Unrooted cuttings
- Vegetables
- Wooden items
- Application for a phytosanitary certificate
- Treatment certificates if needed eg: Fumigation reports, chemical treatment reports etc.
- No Objection letters from relevant Institutes eg: Forest permits etc.
- Test Reports issued by National Plant Quarantine Service eg: Additional Declarations
- Other relevant documents eg: invoice
- Register at National Plant Quarantine Service as an exporter.
- Request made by exporter to obtain Phytosanitary certificate
- Fulfill the import conditions for exporting commodities (lab testing, visual inspection etc:-)
- If require special lab tests has to be done at central laboratories of NPQS (for this a separate request has to be made by the exporter)
- Lab test report is communicated to relevant entry port PQS by NPQS
- Bring entire consignment to Plant Quarantine station.
If Air Freight
- Compliance inspection test to inform the identify of consignment.
- All the boxes should be numbered numbers are clearly mentioned in packing list.
Special requirement for Fruit and Vegetable to Export European Union Country
Some varieties can export only from certified fields for EU Countries
EU Countries are Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Republic of Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece,Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands,Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and the UK.
- Prohibited items to export to EU from Sri Lanka.
Eg:- Soil, Curry Leaves
Amaranthus Spp. ,Mukunuwanna – Temporary
- Following items should be obtained from certified field to export.
- Bitter gourd
- Snake gourd
- Guava
- Mango
- Citrus (require special conditions)
- Commodities that should be accompanied with lab reports from the NPQS
- No Lab reports on export following items to theEuropean Union
- Bitter gourd
- Brinjal
- Elabatu
- Cut flower
If Sea Freight
- for a consignment prior registered with PQS at seaport.
- Either lab tested or not
- If lab tested → test report has to be received by the PQS, Seaport
- Consignment has to be transferred to port premises or shippers go down from factory.
- Request for sample testing by PQS or samples submission for testing (Only to understand the compliance of commodity with document evidence.)
- Sample testing/inspection only if other requirements are fulfilled
- Exporter will receive a notice / approval to load the consignment to ship (prior approval)
- Exporter can submit consignment to vessel – obtain bill of lading.
- Submit bill of lading and application to obtain a PSC to PQS, seaport.
- PSC will be issued based on compliance inspection
- Application for a phytosanitary certificate
- Packing List/Commodity List with correct botanical names
- Treatment certificates if needed eg: Fumigation reports, chemical treatment reports etc.
- No Objection letters from relevant Institutes eg: Forest permits etc.
- Test Reports issued by National Plant Quarantine Service eg: Additional Declarations
- Other relevant documents eg: GAP certification for EU countries
For More Information please contact
Plant Quarantine Station; National Plant Quarantine Services; Cargo Exports – 009411-2260648
Plant Quarantine Station; Airport Cargo Export– 0094112263963
- Application for a phytosanitary certificate
- Treatment certificates if needed eg: Fumigation reports, chemical treatment reports etc.
- No Objection letters from relevant Institutes eg: Forest permits etc.
- Test Reports issued by National Plant Quarantine Service eg: Additional Declarations
- Other relevant documents eg: invoice
A fee of Rs. 162.00 is charged for each consignment.
For more information please contact:
Deputy Director In-Charge,
Plant Quarantine Station,
Bandaranaike International Airport,
Katunayake
Tel: 009411 2252575, 011 2263954
Fax: 009411 2252575
E-mail: phytoquarantine@gmail.com
Certain plants cannot be exported without prior permission from a relevant government agency having legal authority. Following Ordinances and Acts that include gazette notifications issued for amendments, regulations and relevant circulars govern the exportation of plant material:
- Customs Ordinance
- Fauna and Flora Ordinance
- Fisheries and Aquatic resources Act
- Forest Ordinance
- Plant Protection Act
- Consult the relevant authorities for the permission.
- Exportation of live specimens collected from wild and the plants in the protected category is prohibited.
- Consult Conservator General of Forests and or the Director of the Department of wild life for clarifications.
- Registration with the Conservator General of Forests and the Director of the Department of wild life is a requirement for them to issue the permission.
For export – Obtain permission from other institutions
For export Obtain permission from
- Coconut germplasm – The Coconut Research Institute
- Rubber germplasm – The Rubber Research Institute.
- Tea Germplasm – The Tea Development Authority
- Any planting material coming – The Director, Department of Export Agriculture.
under purview of Department of Export Agriculture
| For export | Obtain permission from |
| Coconut germplasm | – The Coconut Research Institute |
| Rubber germplasm | – The Rubber Research Institute. |
| Tea Germplasm | – The Tea Development Authority |
| Any planting material coming under purview of Department of Export Agriculture | – The Director, Department of Export Agriculture. |
- Protected plants (Endemic plants, Red listed plants, CITES listed plants, Plants protected under Flora & Fauna protection ordinance
- Germplasm developed by the Sri Lankan Research Institutes
- For most countries, soil is a prohibited material
- Sample submitted from entry ports to the Plant Quarantine Operations Division
- Registration of intercepted sample with following information.
- Date received
- Name and address of the importer
- Name of the importing country
- Permit number and date
- PSC number and date
- Material and quantity
- Based on the reason for interception, samples of the material are distributed to relevant technical laboratories for further testing.
- Printing and distribution of report format to relevant technical laboratories (entomology/pathology/weed science/treatment technology) to submit the test results.
- Compiling final test reports and final decision to the release of consignment is taking by the Additional Director, National Plant Quarantine Service, Katunayake.
Apart from that questionable material carried by the air travelers are detained at the port of entries and send to Additional Director/ NPQS for destruction.
All items prohibited to import to Sri Lanka are liable to confiscation and destruction. These consignments are destroyed in a manner that is technically justified to be eliminating the associated pest risk under the supervision of the officers of the plant quarantine operation division. The details of the consignments which are subject to destruction are recorded in a separate register.
- The port of Colombo
- The port of Trincomalee
- The port of Mattala
- The port of Hambantota
- The port of Katunayake
- The port of Palaly
- Exfoliated vermiculite
- Ground cork
- Ground peat
- Paper
- Polymer stabilized cellulose
- Saw dust
- Wood and cork shavings
- Spagnum moss
- Bamboo leaves and small shoots
- Cereal leaves, straw, hull and chaff
- Corn and allied plants (Living or dead)
- Cotton and cotton products (including lint waste, seed cotton, cotton seed hull)
- Leaves and stems of plants (living or dead)
- Rice leaves, straw, hull and chaff
- Sugarcane (all parts of the plant, or dead including bagasse)
- Leaves and other parts of banana plants (living or dead)
- Leaves and other parts of coconut and other palm plants (living or dead)
PSC for export
- Issued by the NPPO of the country where products were grown or processed.
- Issued by the NPPO of the country of origin
- describes the consignment
- declares the status of the consignment
- certifying statement,
- additional declarations and
- treatment records,
- May also be issued in certain re-export situations
- If the phytosanitary status of the consignment can be determined by the country of re – export (e.g :- by Inspection)
PSC for re-export
- May be issued by the NPPO of the re – exporting country
- When the commodity was not grown or processed to change its nature in that country and
- Only where an original PSC for export or a certified copy is available.
- link the PSC issued by the country of export
At the request of an exporter
Should be done only in exceptional circumstances
- damage to the Phytosanitary certificate;
- Change of addresses, country of destination or points of entry;
- missing or incorrect information
In all cases,
- should ensure that the original Phytosanitary certificate and any certified copies were returned and cancelled
- The new Phytosanitary certificate should not have the same number
- Number of the original certificate should not be re – used.
- Eg : Phytosanitary certificate lost or in another country
- NPPO may decide to issue a replacement certificate
- should refer to it by including an additional declaration stating that
- “This certificate replaces and cancels phytosanitary certificate no. [insert number] issued on [Insert date]”
• Alternations should be avoided
• They may create uncertainty about the validity of Phytosanitary Certificate
• If alternations are necessary,
– made only on the original Phytosanitary Certificate
– Only by the issuing NPPO
– should be minimal
– should be stamped, dated and countersigned
- If determined to be invalid or fraudulent
- NPPO of the declared country of issuance should be notified as soon possible
- Determining the validity or non – validity of the Phytosanitary certificate in corporation with issuing country
- NPPO of the exporting or re – exporting country should take corrective action and review security of the certificate
- Incomplete, false, misleading, incorrect, conflicting or inconsistent information
- Inconsistent with the model phytosanitary certificates
- Information added by unauthorized persons
- Unauthorized (not stamped, dated or countersigned) alternations or deletions or illegible (e.g. badly written, damaged)
- An expired period of validity
- Non – certified copies
- Transmitted through unauthorized methods etc:-
- Phytosanitary certificate issued for import prohibited article
All import requirements have been met they are dated, signed and stamped, sealed, marked or complete electronically by the NPPO of the exporting or re – exporting country.
A phytosanitary certificate is a document which confirms the health status of a plant material (Plant or plant product) that are exported to a country. The certificate is issued by the NPPO of the country of export confirming required import conditions requested by the country of import.
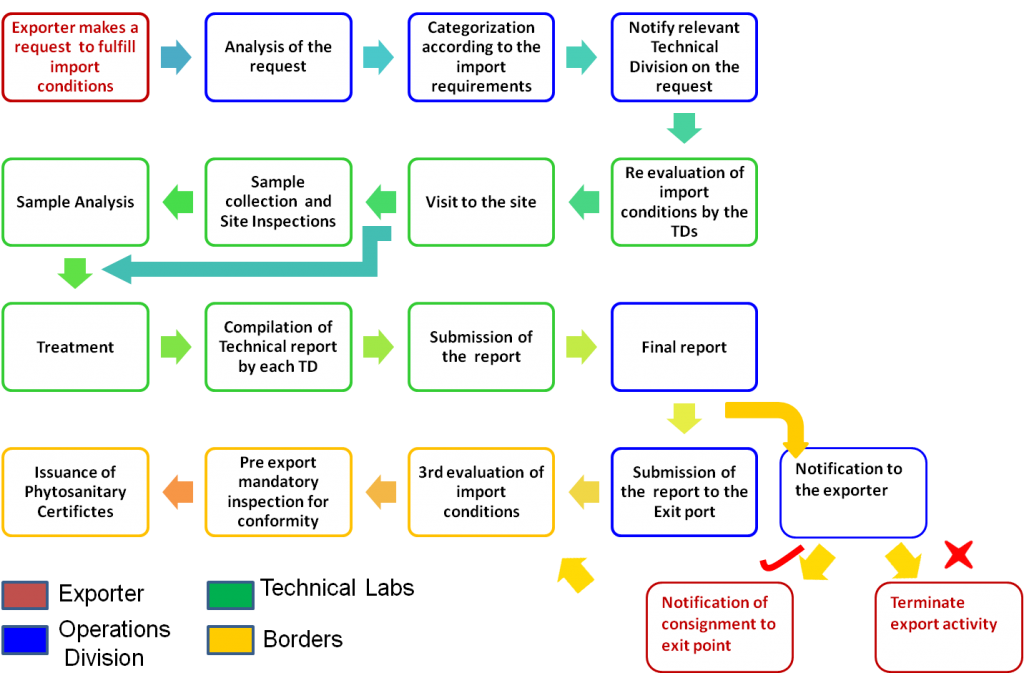
- Please make a request by using an application for phytosanitory certificate for exportaddressing to the Additional Director, National Plant Quarantine Service to fulfill export conditions
- The exporter has to set up a date for inspection of consignment with the agreement of the Plant Quarantine Operations Division.
- Inspection of production premises and sampling are done by the Plant Quarantine Officers
- This is done on the agreed date
- By the officers of relevant technical divisions
- The exporter has to facilitate the official visit and the expenses
- Sampling size is decided by the Plant Quarantine officers based on
- The risk associated with the commodity*
- Importing country requirements
- The type of tests to be performed
- Size of the consignment
- * Sometimes the sampling size may be different for the same commodity based on observable pest symptoms. If the symptoms are obvious, the standard sampling sizes may apply. However, if the symptoms are not obvious, additional sampling may be required to confirm the presence of pests.
e. Depending on the importing country requirements, specific tests may not be required for some commodities for some countries. Those consignments will be either
- Directly submitted to Plant Quarantine Stations at exit ports
- Consignments may associate with official confirmation letters issued by the Additional Director/ NPQS confirming that there is no requirement to perform any laboratory test (Eg: import requirement for freedom from red ring nematode, coconut lethal yellowing etc.).
- Relevant diagnostic tests are done by the technical laboratories of the NPQS. Time taken for the laboratory test may vary depending upon the test type performed.
f. Test reports are combined and a final report will be compiled and issued to OIC/ Plant Quarantine Stations, Airport/Sea port accordingly.
g. Fumigation of consignment if deemed to be necessary (procedure mentioned under the Treatment Technology Division)
h. In parallel, the exporter has to submit an application to the Deputy director, Plant Quarantine Station, (Seaport/ Airport) to obtain a phytosanitary certificate
i. Phytosanitary certificate will be issued to the exporter based on tests reports/ visual inspection done by the plant quarantine officers at the entry port.
- Officers of the Sri Lanka Customs notify the arrival of consignment with a written confirmation to the Plant Quarantine officers at entry ports.
- Documents relevant to the consignment will be inspected by the quarantine officers of NPQS to check whether they comply with the requirements.
- Inspection of consignment by the quarantine inspectors.
- If deemed necessary the consignment shall be subjected to treatment re-export or destruction.
*Entry into Sri Lanka may be denied to any consignment of plant material, which has been imported without required certificate/carries dangerous pathogen/weed/insect or any other pest.
A fee of Rs. 162.00 is charged for each consignment.
- Contain only the information related to phytosanitory matters
– No statement on animal or human health matters, pesticide residues, radioactivity, commercial information (e. g. letters of credit), or quality.
- To facilitate cross – referencing other documents (e. g. letters of credit, bills of lading CITES certificates) may accompany phytosanitary certificate
- All sections should be completed (None, Line blocked out or cut off)
- should be issued before dispatch
- May issue after dispatch of a consignment if:
– The phytosanitary security of the consignment has been assured, and
– NPPO of the exporting country has undertaken sampling inspection and treatments necessary to satisfy phytosanitary import requirements before dispatch of the consignment.
- In the case, the inspection date should be indicated in the additional declaration section if required by the importing country.
- No required information or unable to fulfill requirements
– do not issue a Re – export PSC
- If the country of re – export do not require a PSC but country of destination does
– exporting country may issue a PSC to support re – export PSC or not
– Re – exporting country may issue a PSC of export
* if the phytosanitary import requirements can be fulfilled by visual inspections or laboratory testing of samples
* Country of origin should be indicated in brackets in the place of origin section
- Re – export PSC can be issued if :
– the consignment has been stored, split up, combined with other consignments or repackaged (When combined, all the relevant parts must meet requirements.)
– If a risk of contamination is identified, additional inspection should be carried out
– The Original PSC or its certified copy should accompany the PSC for re – export.
– If the consignment is split up
* PSC for re – export and
* Certified copies of the PSC from the country of export should accompany all such consignments.
Contact Us
- Address : Canada Friendship Road, Katunayake, Sri Lanka
- Email : npqs@doa.gov.lk
- Telephone : +94 11 225 2028/29
- Fax : +94 812 388149
- Open : Mon to Fri - 8.30am to 4.15pm (Closed on weekends & public holidays)